
However, before computing the gain or loss, it is necessary to record the asset’s depreciation right up to the moment of the sale. To illustrate the cost of an double declining balance method asset, assume that a company paid $10,000 to purchase used equipment located 200 miles away. Finally, the company paid $5,000 to get the equipment in working condition. The company will record the equipment in its general ledger account Equipment at the cost of $17,000. These assets are often described as depreciable assets, fixed assets, plant assets, productive assets, tangible assets, capital assets, and constructed assets.

How to calculate DDB depreciation
- The book value of bonds payable is the combination of the accounts Bonds Payable and Discount on Bonds Payable or the combination of Bonds Payable and Premium on Bonds Payable.
- Adjusting entries are recorded in the general journal using the last day of the accounting period.
- When accountants use double declining appreciation, they track the accumulated depreciation—the total amount they’ve already appreciated—in their books, right beneath where the value of the asset is listed.
- This convention provides a balanced method that reduces complexity while maintaining accuracy.
- Various depreciation methods are available to businesses, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
- There are several steps involved in determining whether an impairment loss has occurred and how to measure and report it.
In summary, understanding Bookkeeping for Chiropractors double declining balance depreciation is crucial for making informed financial decisions. It’s a method that can provide significant benefits, especially for assets that depreciate quickly. Various software tools and online calculators can simplify the process of calculating DDB depreciation.
DDB is an Accelerated Method of Depreciation

In summary, the choice of depreciation method depends on the nature of the asset and the company’s accounting and financial objectives. An asset account which is expected to have a credit balance (which is contrary to the normal debit balance of an asset account). For example, the contra asset account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is related to Accounts Receivable. The contra asset account Accumulated Depreciation is related to a constructed asset(s), and the contra asset account Accumulated Depletion is related to natural resources. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as bookkeeping December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position.
What Is Fixed Asset Accounting? 4 Things You Need To Know
- If you’re calculating your own depreciation, you may want to do something similar, and include it as a note on your balance sheet.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement.
- A balance on the right side (credit side) of an account in the general ledger.
- The carrying value of an asset decreases more quickly in its earlier years under the straight line depreciation compared to the double-declining method.
Employing the accelerated depreciation technique means there will be lesser taxable income in the earlier years of an asset’s life. Salvage value is the estimated resale value of an asset at the end of its useful life. Book value is the original cost of the asset minus accumulated depreciation.
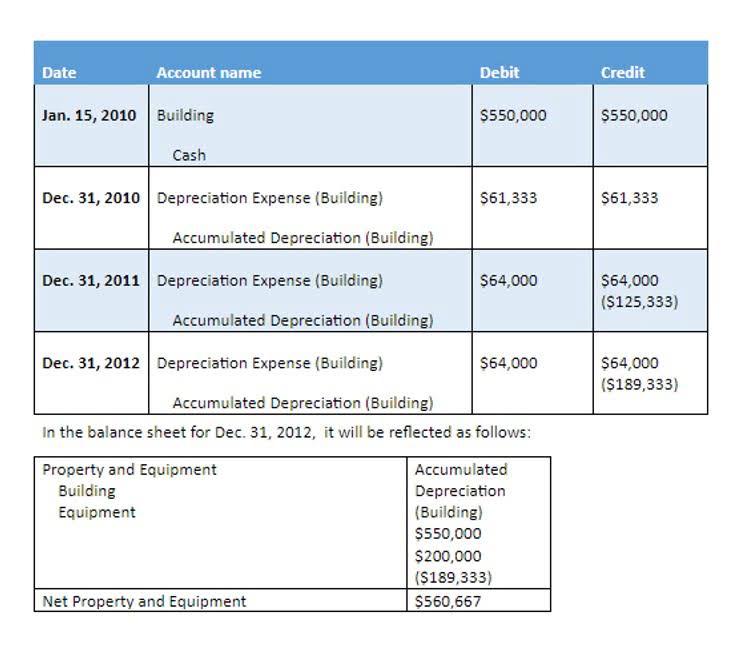
In contrast to straight-line depreciation, DDB depreciation is highest in the first year and then decreases over subsequent years. This makes it ideal for assets that typically lose the most value during the first years of ownership. Double declining balance depreciation is a method of depreciating large business assets quickly. Under the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for public companies, expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenue that is earned as a result of those expenses. This account balance or this calculated amount will be matched with the sales amount on the income statement.
- The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position.
- The double-declining balance depreciation (DDB) method, also known as the reducing balance method, is one of two common methods a business uses to account for the expense of a long-lived asset.
- Also, if you want to know the other essential bookkeeping tasks aside from fixed asset accounting, you can read our piece on what bookkeeping is and what a bookkeeper does.
- Let’s assume that a retailer purchases fixtures on January 1 at a cost of $100,000.
- The company will have less depreciation expense, resulting in a higher net income, and higher taxes paid.
Step 1: Compute the Double Declining Rate

Accelerated depreciation is any method of depreciation used for accounting or income tax purposes that allows greater depreciation expenses in the early years of the life of an asset. Accelerated depreciation methods, such as double declining balance (DDB), means there will be higher depreciation expenses in the first few years and lower expenses as the asset ages. This is unlike the straight-line depreciation method, which spreads the cost evenly over the life of an asset. The double declining balance method differs from other common depreciation techniques, such as straight-line and units of production methods.
Yorum Yaz
Sign in to post your comment or sign-up if you don't have any account.